The Economics of Intrigue: How Dark Web Trade Networks Work

This tech age has ushered in a variety of new markets, but few are as puzzling and controversial as the dark web markets. Concealed from the invasive eyes of traditional browsing, these marketplaces thrive in the underbelly of the internet, often conducting business that questions legal and moral boundaries. Cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin allow secretive operations the capacity to flourish, allowing users to purchase and sell everything from artwork to illegal substances with a degree of privacy that traditional markets simply cannot offer.
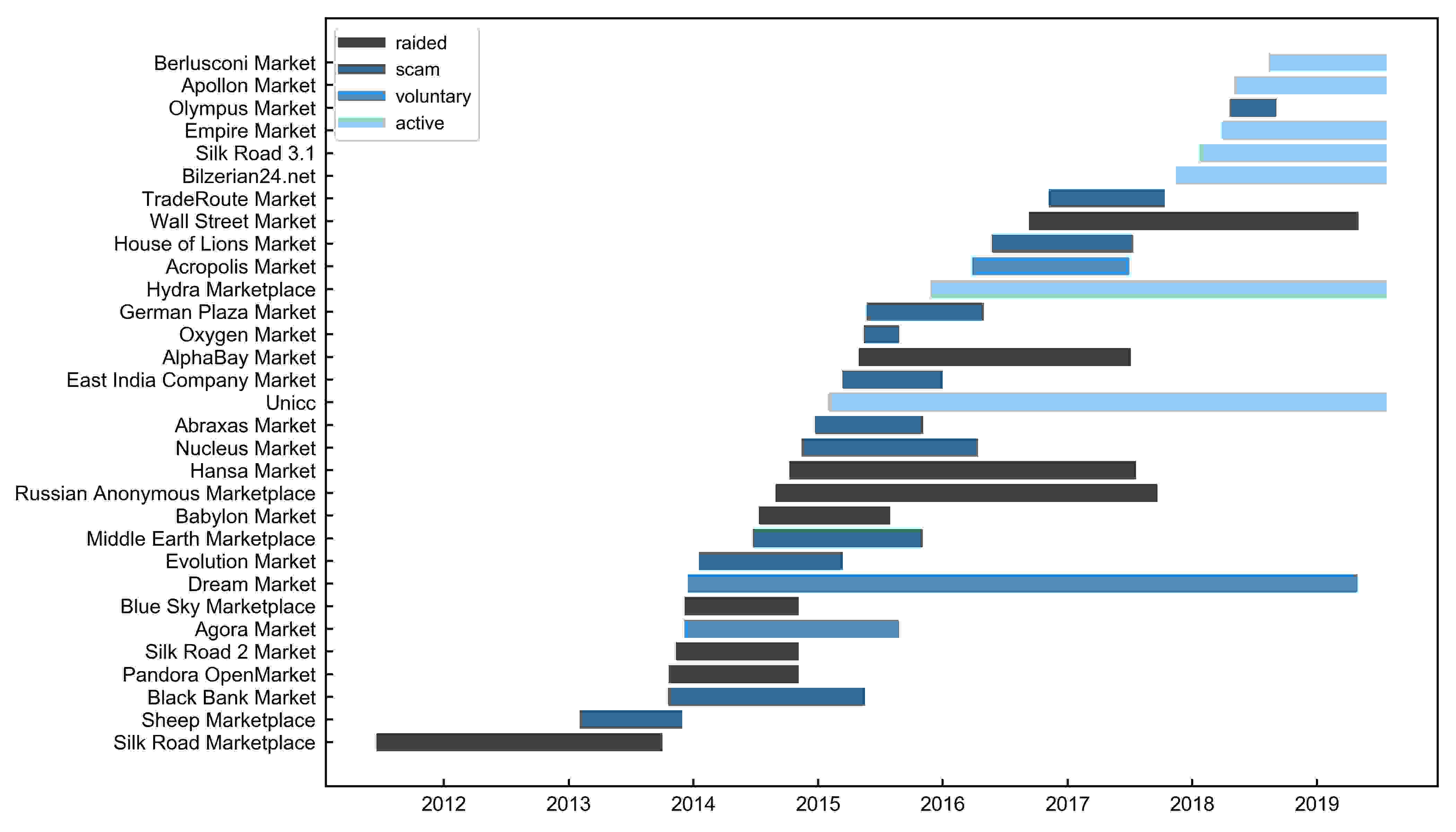
Exploring the deep web is not for the weak. The hidden internet, as it is commonly called, requires distinct software to enter, and even then, it presents many risks, including scams and legal consequences. The appeal of these hidden platforms lies not only in the availability of rare items but also in the sense of community they encourage among users who share a distrust of the mainstream internet. dark markets investigates the intricate workings of dark web markets, exploring how they operate, the culture that envelops them, and the impact for those who decide to engage in this covert economy.
Understanding the Dark Web
The dark web refers to a section of the web that is not at all indexed by conventional search engines, rendering it accessible only through particular software and configurations. Typically, users access it via the Tor network, which conceals their online actions and allows for both privacy and, in numerous instances, illicit behaviors. This covert space hosts a variety of marketplaces, forums, and communication platforms that support various activities, both legal and illegal.
One of the most notable aspects of the dark web is its use for anonymous transactions. Users often participate in the buying and selling of goods and services that are hard or impossible to find on the surface web, including controlled substances, arms, stolen data, and counterfeit currency. Cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin are frequently utilized in these transactions to enhance anonymity, granting a layer of protection for both buyers and vendors. This financial aspect has led to a complex ecosystem where trust and reputation play crucial roles in market dynamics.
While the shadow web is often linked with illegal activities, it is also a location for free expression, particularly in regions where censorship is common. Advocates, journalists, and whistleblowers frequently use dark web tools to connect safely and disseminate information without fear of retribution. This duality highlights the shadow web's multifaceted nature, existing as a refuge for certain freedoms while concurrently being a platform for nefarious dealings.
The Economic Principles of Dark Web Marketplaces
Darknet markets operate within a unique economic framework that differs sharply with conventional marketplaces. Such platforms primarily thrive on privacy, enabled by technologies like the Tor network that obscure user identities and locations. The need for confidentiality often arises due to the illegal nature of many items and services traded, such as drugs, weapons, and hacked information. This setting creates a demand-driven economy where sellers are able to set prices based on the assumed risk associated with their products and the anonymity of their buyers.
The market competition in darknet markets is shaped by a diverse range of vendors, each attempting to gain buyers' attention through reviews, product quality, and price tactics. Vendors often utilize escrow services to build trust among buyers despite the inherent uncertainties of online transactions. Additionally, digital currencies play a significant role in the dark web, as they offer an additional layer of anonymity and security, which enhances sales and transactions beyond conventional banking systems.
In spite of their illicit nature, darknet markets exhibit features similar to legal economies, including demand and supply principles, advertising tactics, and client service methods. Some vendors allocate resources in advanced logistics to ensure timely delivery of goods, while others concentrate on cultivating trust through consistent positive interactions with buyers. Overall, the financial aspects of these marketplaces reveal a complex interplay of anonymity, risk, and competition that influences how they function and evolve.
Risks and Legal Consequences
Involvement with dark web markets carries substantial risks for individuals. Buyers may encounter frauds, receiving fraudulent goods or nothing at all after payment is made. Furthermore, personal data can be vulnerable to malicious actors, leading to identity theft or monetary fraud. The concealment that dark web markets offer can quickly be breached, putting users at risk.
The legal implications of participating in these markets can be serious. Many goods and services traded on the darknet, such as illicit drugs, weapons, and stolen data, are banned by law. Law enforcement agencies actively watch these platforms, employing advanced techniques to identify users. Individuals caught buying or selling prohibited items can face substantial fines and criminal charges, with potential prison sentences depending on the severity of the offense.
Additionally, even if a person does not participate in illegal activities personally, merely visiting dark web markets can lead to unwanted legal attention. In many jurisdictions, this can create suspicion and prompt investigations. Therefore, the potential consequences of investigating these markets extend further than the immediate actions taken, affecting long-term personal and professional lives.
